For some reason, you might be curious about how long does THC stay in the system or how long does marijuana stay in urine. Just like other drugs, the amount of time the cannabis’ THC components remain in an individual’s system may vary according to several factors such as the method of testing, the way it is consumed, frequency of usage, THC’s potency, and other factors relating to the body such as metabolism, and hydration.
As we go through this article, we’ll find out what THC is, its contents, detectable windows, and ways to detoxify or eliminate its remains in the system.
What is THC?
With the legalization of marijuana in an increasing number of states, it’s almost certain that you’ve heard the term THC and other cannabis-related stuff from people of different places; you may even wonder what these terms refer to. Well, here’s a briefer we’ve prepared just for you.
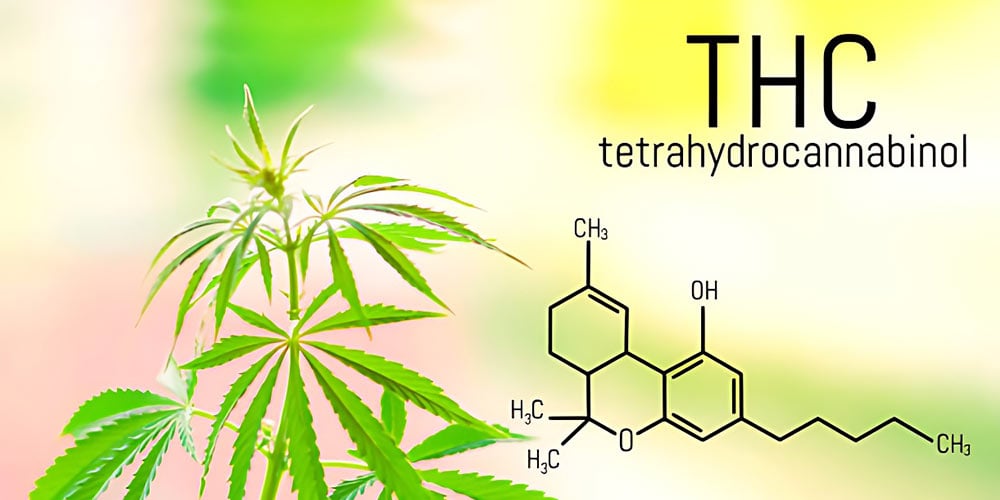
The cannabis plant produces a viscous liquid that is usually rich in cannabinoids. The plant contains more than 100 of these compounds, responsible for the high sensation it makes after a few minutes of usage. The THC, scientifically referred to as tetrahydrocannabinol, is a mind-altering chemical found primarily in the cannabis plant.
The body’s endocannabinoids share the same chemical structure with THC; this allows the THC to interact and alter the brain’s cannabis receptors. According to NIDA, THC triggers the human brain cells to release dopamine, resulting in a feeling of bliss. It also affects how the hippocampus—a brain region involved in creating new memories–-processes information.
How Does the Body Process THC?
After intake through weed smoking, edible or other methods, the THC is converted by the liver into 11-hydroxy-THC and carboxy-THC, which is absorbed by the human tissues and organs, including the brain, heart, and fat (metabolites). 20% of cannabis leaves the body through urine, and about 65% is eliminated through feces. What remains of this is automatically stored in the body’s fatty tissues, which are eventually released into the bloodstream and processed by the liver.
Factors that Influence THC Detection in the System
The majority of the research conducted agreed that cannabis may linger in the human body for up to 30 days after last use and can even be detected in hair follicle drug tests for several months after. This considerable detection variation is caused by various factors that can alter the THC’s detection window. The following six elements can affect how long cannabis remains in your bloodstream.
The amount of THC Ingested – although the potency of the weed used should also be taken into account, it is most likely that the more THC a person consumes, the longer it would take for the body to break down and eliminate the compound from the system.
The method used to ingest the compound – technically, THC reaches the organs and bloodstreams faster when inhaled than when ingested.
Dosage or frequency of use – The more THC you consume, the longer it will take for your body to break down and eventually eliminate its contents from your system. However, you also need to consider the type of marijuana you consume since other strains of marijuana are stronger than others.
Genetics – Genetic makeup can also affect how long marijuana contents stay in the bloodstream. Some people find it relatively faster to clear their system of marijuana contents due to variations of certain enzymes, which is often an awesome hereditary feature.
Metabolism – Normal physiological processes also help the body get rid of marijuana and its compounds. A person with a fast metabolism is said to most likely be able to flash out marijuana and its active metabolite faster than a person with a sluggish metabolism. This only means that if your metabolism is high, your detection window will probably be much less than average.
Type of drug test administered – marijuana detection may depend significantly on the kind of method used to detect its presence–which we will elaborate on in the following section.
How Long Does it Take Weed to Leave Your System?
Scientists believe that THCs naturally have a very long half-life—the period it takes for the THC compound to decrease by half. THC remission usually varies on an individual’s marijuana use. THC half-life for sporadic weed users was calculated to be around 1.3 days. Frequent users, on the other hand, frequent users may exhibit a Half-life that may range from 5 to 13 days.
Besides the frequency of use, THC detection also varies on the kind or method of test undertaken. Below are the general estimates of each type of cannabis test:
Saliva Test. A tongue swab is a kind of non-invasive rapid drug test in which a sample is usually taken from either the tongue or the inside of the cheek through a sponge or other absorbent pad. According to research, saliva testing can detect cannabis use anywhere from 24-72 from the last use.
Urine Test. Urine samples can hold the maximum concentration of THC for the longest time. However, it is the most preferred drug test method because of its ability to detect cannabis approximately 3–30 days after use, depending on the person’s frequency of weed use.
Hair Test. According to a study, a hair test is most accurate for identifying daily cannabis users and may not be reliable for detecting light users. However, the detection window for hair testing is broad and is also said to be capable of detecting about 90 days or three months from the use of marijuana.
Blood Test. Cannabis compounds remain in the bloodstream for only a brief period and may decline 3-4 hours after ingestion; hence, this type of test isn’t used widely for drug testing purposes.
How to Get Cannabis Out of the System?
Basically, there are only two possible approaches that can be used to effectively lower or rid the cannabis’ THC contents from the body, and these are: (1) the lowering of THC content intake; and (2) the accelerating of metabolism. Although there exists no proven way to speed up metabolism, getting some exercise might help the body be able to metabolize more THC contents.
Additionally, drinking more water may help ease an incredibly high THC level.
How Long Does THC Stay in the System: The Conclusion
While the intoxication of weeds can last up to 6 hours, its compounds, particularly the delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)–responsible for its euphoric-like effects–can stay in the system for a period (determining how long it can linger in the system is an exact science). For the most part, cannabis is difficult to totally rid of the human body. This is because most cannabinoids, including THC, are stored in fat cells and are only slowly released from the body’s fatty tissues.
THC generally serves as a psychoactive ingredient that can be detected in hair for up to 90 days (or more) from the last usage. On the other hand, blood can store THC contents for up to 24 to 48 hours, 24 to 72 hours for saliva, and urine for up to 3 to 30 days, depending on a person’s water intake.