Cannabis growers often face challenges related to marijuana nutrient deficiencies and abnormalities in cannabis leaves. Fortunately, there are effective solutions to common issues such as unusual spots on leaves, yellowing of marijuana leaves, or the entire plant turning yellow. A proper nutrient system formulated for plants like tomatoes can help address these cannabis leaf deficiencies.
While utilizing appropriate nutrients for cannabis can prevent deficiencies, it’s also crucial to maintain the proper pH level to avoid nutrient-related issues and leaf abnormalities. If cannabis-friendly nutrients are being used, but unusual spots or yellowing of leaves persist, it’s likely due to the pH level, and prompt action should be taken to address the issue.
Most Common Marijuana Nutrient Deficiencies and Solutions
In this portion, we will list the most common marijuana nutrient deficiencies and some possible solutions you can do to prevent these nutrient deficiencies. It will also include the early signs and what to look for when assessing marijuana nutrient deficiencies.
Nitrogen Deficiency
Nitrogen deficiency can occur due to a lack of nitrogen in the soil, but it can also happen because of pH issues. When the soil is too acidic, it can lock up the nitrogen and make it unavailable for the plant to use. In such cases, adjusting the soil’s pH level may help the plant access the nitrogen it needs.
Overwatering can also cause nitrogen deficiencies by reducing oxygen levels in the soil and preventing the roots from absorbing nutrients effectively. It is essential to monitor soil moisture levels and only water the plant when the top layer of soil feels dry to the touch.
Overfeeding with phosphorus or potassium can also lead to nitrogen deficiencies since these nutrients can compete with nitrogen for uptake by the plant. Therefore, it is crucial to provide a balanced nutrient solution that includes all the necessary macronutrients in the correct proportions to prevent nutrient deficiencies.
How to Prevent Nitrogen Deficiency
You can find various pre-mixed nutrients containing nitrogen at the store or opt for nitrate of soda or organic fertilizers, which are excellent nitrogen sources. Almost all types of plant nutrients contain nitrogen. If you haven’t been providing any nutrients to your plants, try supplementing your regular nutrients with more nitrogen to see if the plant recovers.
However, if you have already been using nutrients, the plant is unlikely to have a nitrogen deficiency. Suppose the signs of a spreading nitrogen deficiency persist even after supplementing with nitrogen for a week or two. In that case, you need to identify the underlying cause of the yellowing to address it.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants can cause various symptoms, such as affecting the lower and older leaves, darkening, yellowing, and developing bronze or brown spots. Red stems may or may not be present, and yellowing is not an initial sign. A calcium deficiency usually accompanies this type of deficiency.
The deficiency is more commonly observed during the flowering stage when buds start forming, but it may also occur during the vegetative stage, beginning with the lower and oldest leaves. Adequate phosphorus is crucial for cannabis plants to thrive during the flowering/budding phase, and standard nutrients for flowering plants usually contain enough phosphorus. A phosphorus deficiency is identified by the second number on most nutrient bottles and is often associated with symptoms of a calcium deficiency.
How to Prevent Phosphorus Deficiency
If your cannabis plant exhibits symptoms of phosphorus deficiency, the pH at the roots may be too high or low, affecting phosphorus absorption. To remedy this, it is necessary to flush the system with properly pH’d water and nutrients. For cannabis grown in soil, a root pH of 6.2-7.0 is optimal, while for hydroponics, it should be 5.5-6.2. Maintaining a proper nutrient balance and avoiding excess iron and zinc can also help prevent phosphorus deficiency. After correcting the deficiency, new leaves should not exhibit the symptoms, but previous leaf damage may not recover. Monitoring the plant for improvement is essential.
Potassium Deficiency
Typically, symptoms of a marijuana potassium deficiency appear on older leaves, but sometimes they can also occur at the top of the plant. Leaves affected by potassium deficiency show yellow, brown, or burnt edges and tips. The burnt edges can resemble nutrient burn, but the affected leaves also turn yellow at the margins. You may observe either the brown burnt edges or the yellowing first. When both symptoms are present, it indicates a potassium deficiency.
Although plants may stretch and stems may weaken, the symptoms are more prominent in the leaves. They resemble an iron deficiency in that they turn bright yellow, but the tips of the leaves curl, while the edges turn brown, burn, and die.
It’s important to ensure your grow lights are at an appropriate distance from your plants to avoid any potential sunburn. Suppose you suspect that your plants may be suffering from a potassium deficiency. In that case, addressing it quickly with a nutrient solution containing potassium or adding potassium-rich amendments to your soil is important. However, it’s also important to remember that other nutrient deficiencies or issues, such as overwatering, can exacerbate a potassium deficiency. Hence, it’s important to consider all potential factors when diagnosing and treating plant issues.
How to Prevent Potassium Deficiency
When growing cannabis plants, it is important to ensure that any issues with the plant are not due to light burn, which can often look like a potassium deficiency. To prevent a light burn, powerful lights like LED or MH/HPS should be kept at a minimum distance of 12 inches, and most models should be kept even further away.
Potassium deficiencies are less likely to occur if quality soil or cannabis-friendly nutrients are used but can occur if heavily filtered or RO water is used. Potassium is best absorbed at lower pH ranges, so adjusting the pH to the appropriate range can also help with deficiencies.
In addition, when a potassium deficiency is suspected, flushing the system with clean, pH’d water and regularly adding cannabis-friendly nutrients may help. It is important to watch the plant over the next few days to ensure the problem does not spread to new growth.
Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is an essential nutrient that provides structure to the cannabis plant and helps it withstand stress. A calcium deficiency in cannabis plants is characterized by brown or bronze splotches or spots on the leaves, which may occasionally appear purple under LED grow lights.
Yellowing may also occur, but only sometimes. Calcium deficiencies are often caused by low pH at the roots and can also be associated with growing in coco or using soft or filtered water. Calcium is a semi-mobile nutrient and moves slowly through the plant, tending to show up on actively growing leaves exposed to light.
It is common to see calcium deficiencies in newer growth, especially on the parts of fan leaves that are exposed to light. It is important to monitor calcium levels in cannabis plants to ensure healthy growth and optimal yields.
How to Prevent Calcium Deficiency
It’s important to note that a calcium deficiency can also be caused by over-fertilization or the use of hard water that contains high calcium levels, which can lead to a nutrient lockout. In these cases, flushing with pH’d water and reducing nutrient use may also help to correct the issue.
To prevent a calcium deficiency from occurring in the first place, it’s important to maintain a proper balance of nutrients and pH levels in your growing medium. Calcium is often included in cannabis-friendly nutrient solutions, but following the recommended dosage is important to avoid over-fertilization. Additionally, using filtered or reverse osmosis water can help to prevent nutrient lockout caused by hard water.
If you are growing in soil, you can add calcium to your growing medium using products like gypsum, dolomite lime, or bone meal. These products slowly release calcium into the soil over time, helping maintain healthy plant calcium levels.
Maintaining the proper pH and nutrient balance in your growing medium can help prevent calcium deficiencies and other nutrient imbalances in your cannabis plants, leading to healthier and more robust growth.
Magnesium Deficiency
Yellowing, reddening of lower and older leaves, and light green coloring on veins and edges are classic signs of cannabis magnesium deficiency. If promptly addressed, this deficiency can prevent the plant from losing many lower leaves as magnesium is transferred from old leaves to new ones. The edges of the leaves may become yellow or bright green and feel crispy to the touch, which is different from nutrient burn. In severe cases, light brown spotting may also occur.
How to Prevent Magnesium Deficiency
Supplementing plants with calcium-rich materials like agricultural lime or eggshells without magnesium can cause magnesium deficiency in cannabis. Proper cannabis nutrients can prevent this deficiency. Even with good nutrients, cannabis plants may exhibit a magnesium deficiency if the root pH is too low, especially in hydroponic systems. This is because low root zone pH hinders magnesium absorption, despite its presence in the medium. Thus, maintaining the correct pH range and avoiding excessive acidity is crucial in preventing magnesium deficiency.
Iron Deficiency
Cannabis iron deficiency manifests initially on bright yellow new leaves and can occur with other nutrient problems or deficiencies. pH problems primarily cause it, but it can also be due to environmental stress, which can clear up.
The primary symptoms of this deficiency are the complete yellowing of new leaves and yellow portions that can later turn green as the plant grows. Unlike most other deficiencies, an entire leaf can regain its healthy green color. It is similar to magnesium deficiency but affects newer leaves, unlike magnesium deficiency, which affects older ones.
How to Prevent Iron Deficiency
To avoid iron deficiency in cannabis, adjust pH to the appropriate range, which is 6.0-6.5 in soil and 5.5-6.5 in coco coir or hydro. Iron gets locked out at higher pH levels, and excess calcium and magnesium can also trigger iron deficiency symptoms.
Flushing with pH’d water can help restore pH levels. Most tap water and quality soil or nutrients already contain enough iron, and adding a Cal-Mag supplement can prevent deficiencies. Watch for improvement in new growth within a week after addressing the issue.
Manganese Deficiency
A manganese deficiency in marijuana plants can cause the yellowing of leaves between veins, mottled brown spots, and stunted growth. The yellowing starts at the base of the leaves and spreads towards the tips. Leaves may also shred and fall apart.
How to Prevent Manganese Deficiency
If your cannabis plant shows signs of a manganese deficiency, it may have yellowing leaves with brown spots and stunted growth. The problem can be caused by high pH or excess iron. Manganese is best absorbed by the roots in the 6.0-7.0 pH range for soil and the 5.5-6.0 pH range for hydro. To correct the issue, flush the system with clean, pH-adjusted water containing cannabis-friendly nutrients with manganese. Avoid high pH ranges to prevent manganese deficiencies. Damaged leaves may not recover.
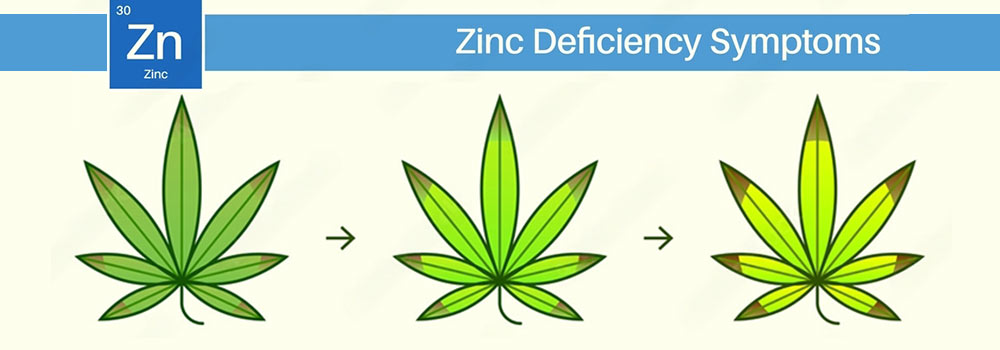
Zinc Deficiency
A zinc deficiency in cannabis can cause the yellowing of younger leaves between the veins, with discolored tips that may die off. The plant may exhibit stunted vertical growth, bunched leaves with a banded appearance, and bud growth may stop or decline if left untreated.
How to Prevent Zinc Deficiency
It’s important to note that if the zinc deficiency persists or worsens despite your efforts to correct the pH and nutrient levels, you may need to consider other factors contributing to the problem, such as pests or diseases. In such cases, seeking advice from experienced growers or a professional consultant may be helpful to help identify and address the underlying issues.
Additionally, it’s always a good practice to regularly monitor your plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies or other problems, as early detection and intervention can often prevent more serious issues.
Copper Deficiency
Copper deficiency in cannabis causes dark leaves with blue or purple undertones and pale yellow or white tips and edges. Correcting the deficiency promptly during flowering is crucial as buds may stop maturing.
Copper is “low-mobile,” and affected leaves may not revert to green, but the problem should not spread to new leaves. Symptoms include a metallic sheen, stiff leaves turning under, and slow bud growth, different from a nutrient burn that causes brown or burnt tips.
How to Prevent Copper Deficiency
To correct a copper deficiency in cannabis, adjust the pH to the appropriate range, which is slightly acidic, for better absorption. Flushing with pH water containing nutrients can help restore the pH. Most growers don’t need to add more copper since it is in tap water and contains cannabis-friendly nutrients. Overwatering or root problems can also cause deficiencies. Watch for leaf recovery after implementing solutions, but old growth may not fully recover.
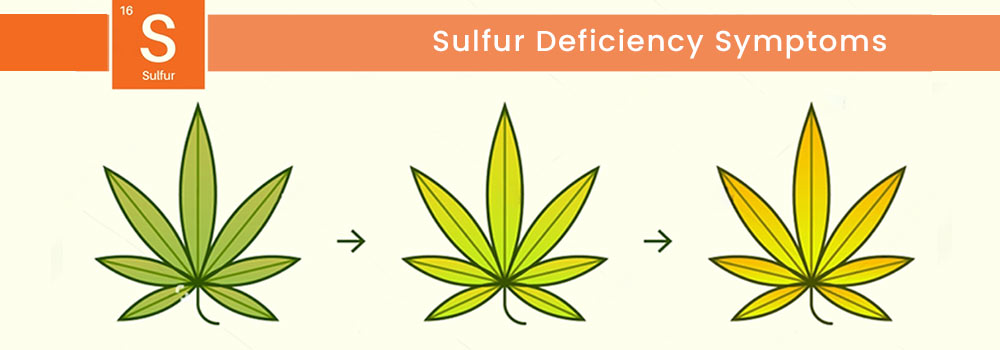
Sulfur Deficiency
Sulfur deficiency in cannabis is uncommon and causes all-over chlorosis, beginning with newer leaves, and may resemble nitrogen deficiency. The underside of leaves may turn pinkish-red or orange, and buds may wither during flowering. Unlike other deficiencies that start at the tips, sulfur deficiency begins at the back of the leaf and moves forward.
How to Prevent Sulfur Deficiency
To address sulfur deficiency in cannabis, check and adjust the pH to prevent lockout. Since sulfur moves slowly through the plant, it may take several days before improvements are observed after correcting the pH.